IPM
Integrated Pest Management
Principles of Integrated Pest Management
1. Inspection
There are 2 types of IPM inspections. The first is an initial, detailed inspection that serves as the starting point for the IPM program. The second type is an ongoing (often-monthly) inspection used to determine if any pests are present and if any pest management action may be needed to control or discourage pests.
2. Identification
biological control, habitat manipulation, modification of cultural practices, and use of resistant varieties.
3. Monitor
Monitoring should include walk-through visual inspections, monitoring traps, interviews with staff and occupants, and reviewing pest- sighting logs.
4. Threshold
The level at which a pest causes sufficient damage to warrant public health attention and intervention. Real or perceived damage can be aesthetic and can have economic, psychologic, and medical consequences.
5. Treatments
should consider the cultural/sanitation practices, physical/mechanical controls, biological controls, and least toxic pesticides such as baits, gels and traps available. Use of pesticides should be justifiable based on pest sighting logs, type of pest, and pest response to nonchemical methods.
6. Evaluation
perform an assessment in order to determine the root cause of the infestation and success or failure of the action taken. The evaluation will determine if further action is needed to meet the objectives and whether or not there are other areas in the building that may be vulnerable to infestation and need to be monitored or altered. After the evaluation and the IPM objectives have been met, the IPM plan should be updated to include any changes in procedure.
SCOPE OF WORK
Initial IPM Inspection:
 AL KANANA PEST CONTROL will conduct initial interior and exterior inspection and provide a written report that identifies problem areas and recommends structural, sanitary and/or procedural modifications to reduce pests’ access to food, water and shelter.
AL KANANA PEST CONTROL will conduct initial interior and exterior inspection and provide a written report that identifies problem areas and recommends structural, sanitary and/or procedural modifications to reduce pests’ access to food, water and shelter.
IPM Monitoring Plan:
AL KANANA PEST CONTROL will submit a monitoring plan for building manager approval in advance of any contracted work. The plan will include:
1. An ongoing monitoring proposal for all locations where there is an active infestation, pest evidence or conditions potentially leading to infestation
2. Meetings or calls after treatment of infested areas
3. Recommended procedures for unit turnover
IPM Identification:
involves confirming the type or species of a pest (for example, a mouse versus a rat; a German cockroach versus a brown-banded cockroach). Once the pest is identified, habitat modifications may greatly reduce the infestation. These habitat modifications may include making repairs, cleaning, removing standing water, and removing clutter.

IPM Threshold:
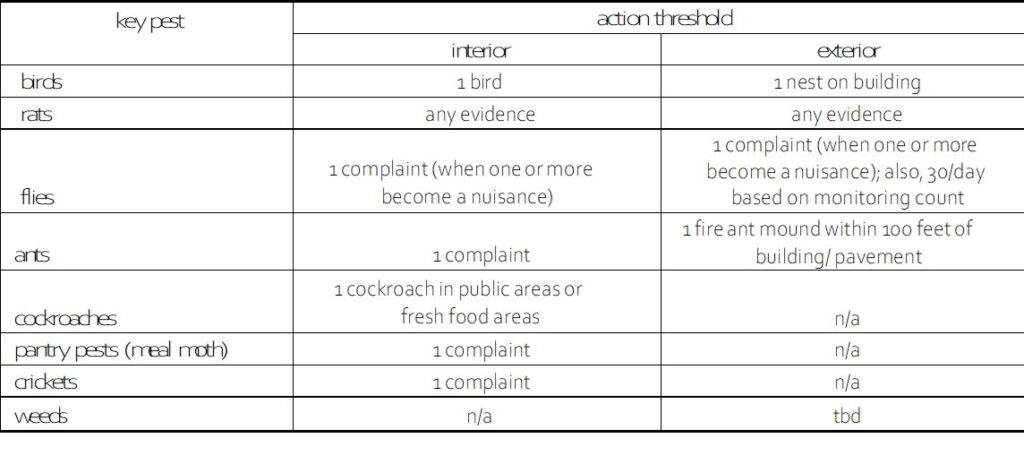
Sampel for Key Pests and Action Thresholds:
IPM Treatment:
Service Descriptions
Insect Control
 i. Application of Insecticides to Cracks and Crevices: Insecticides will be applied ONLY in “crack and crevice” treatments. Formulated insecticide will not be visible to a bystander during or after the application process.
i. Application of Insecticides to Cracks and Crevices: Insecticides will be applied ONLY in “crack and crevice” treatments. Formulated insecticide will not be visible to a bystander during or after the application process.
a. All labor and materials will be furnished to provide control of roaches, ants, silverfish and rodents.
b. All harborage areas (i.e., cabinets, sinks, closets, pantries) and cracks, crevices and breeding sites where pests have been identified will be treated with roach bait gels.
c. Roach bait gels will be odorless, non-volatile and will not produce airborne particles. They will be designed for use in sensitive areas and residents will not need to remove edibles or dishes from cabinets or vacate premises during application.
d. During each service visit, special attention will be paid to kitchen and bath areas, including spaces beneath sinks, counters, appliances, etc.
 AL ii. Application of Sprays or Insecticides to Exposed Surfaces: Fogging is prohibited and the application of spray insecticides to exposed surfaces will be limited. If use is required, AL KANANA PEST CONTROL will obtain approval from the building manager prior to any application of insecticide to an exposed surface or application of a spray treatment.
AL ii. Application of Sprays or Insecticides to Exposed Surfaces: Fogging is prohibited and the application of spray insecticides to exposed surfaces will be limited. If use is required, AL KANANA PEST CONTROL will obtain approval from the building manager prior to any application of insecticide to an exposed surface or application of a spray treatment.
KANANA PEST CONTROL will ensure resident and employee safety and employ necessary precautions for the containment of the pesticide to the site
of application. No surface application or space spraying will be conducted while resident(s) or personnel are present.
iii. Insecticide Bait Formulations: Bait formulations will be the standard pesticide technology for cockroach and ant control, with alternate formulations restricted to unique situations where baits are not practical.
iv. Monitoring: Sticky traps will be used to guide and evaluate indoor insect control efforts where necessary
Rodent Control
i. Trapping: AL KANANA PEST CONTROL will use trapping as the first method of indoor rodent control. Traps will be out of general view and in protected areas so as not to be affected by routine cleaning and other operations. AL KANANA PEST CONTROL will check trapping devices on a schedule approved
by the building manager. All trapped rodents and all rodent carcasses will be disposed of in an appropriate manner.
ii. Use of Rodent Bait (rodenticides): When used in conjunction with other structural and mechanical controls, rodent baits are an effective means of providing long-term control with a minimal risk to people, pets and wildlife. AL KANANA PEST CONTROL must obtain building manager’s approval prior to starting any interior rodenticide treatment. When used indoors, baits will always be installed within tamper-resistant bait stations and in out-of-reach areas.


All bait stations (inside and outside) will be maintained in accordance with the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) regulations, with an emphasis on the safety of non-target organisms and in adherence to the following:
a. All bait stations must be placed out of general view, in locations where they will not be disturbed by routine operations.
b. The lids of all bait stations must be securely locked or fastened shut.
c. All bait stations must be securely attached or anchored to the floor, ground, wall or other immovable surface so that the box cannot be picked up or moved.
d. The bait must always be secured in the feeding chamber of the bait station and never placed in the runway or entryways of the bait station.
e. All bait stations must be labeled on the inside with AL KANANA PEST CONTROL’s business name and address, and dated by AL KANANA PEST CONTROL at the time of installation and at each follow-up service.
f. All bait stations should be numbered and their location marked on a simple floor plan map. AL KANANA PEST CONTROL should leave a copy of the map along with the pesticide’s label with the building manager.
g. Bait stations should be inspected during every service visit for monitoring purposes and to ensure stations are not providing harborage to non-target pests.


